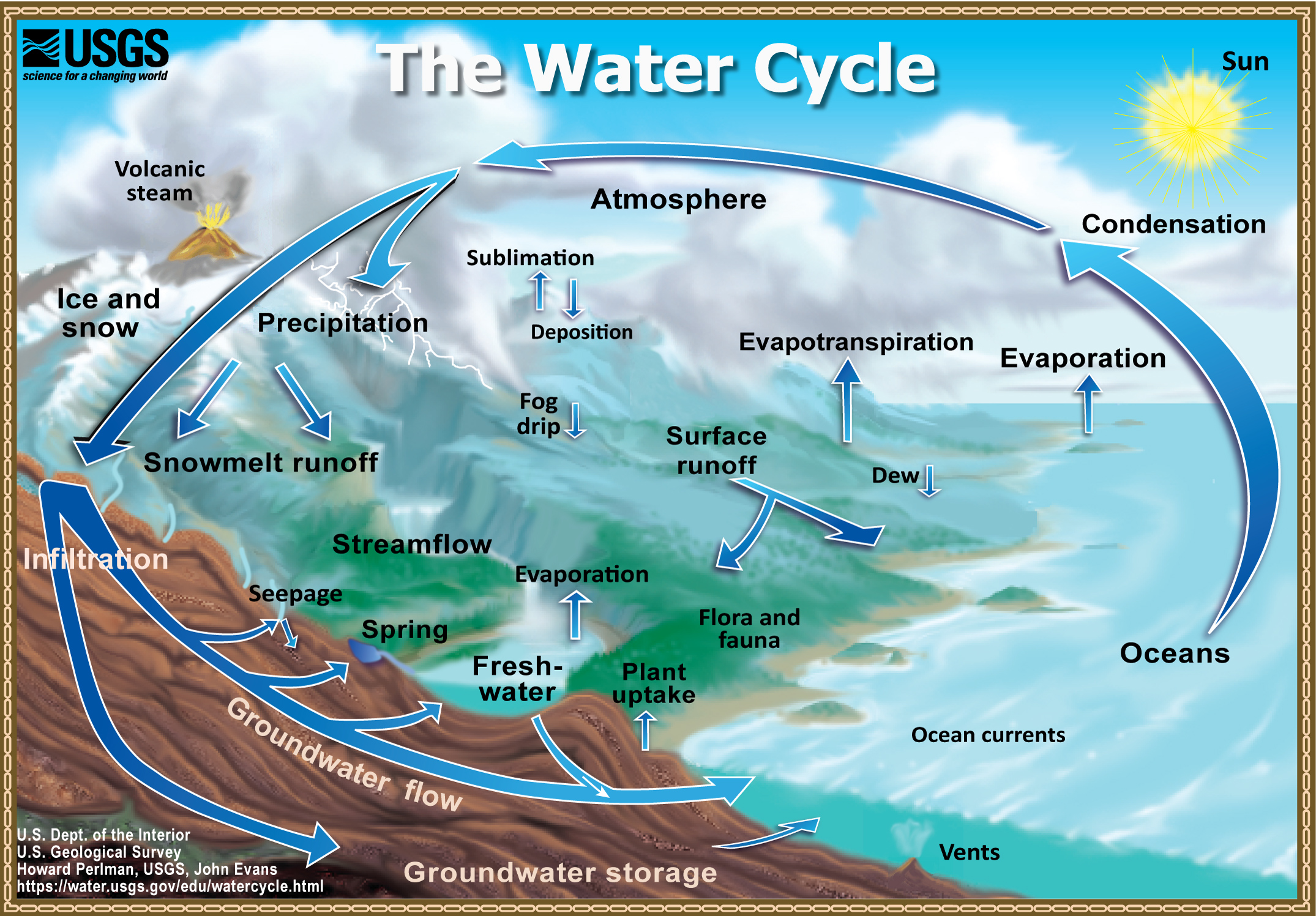
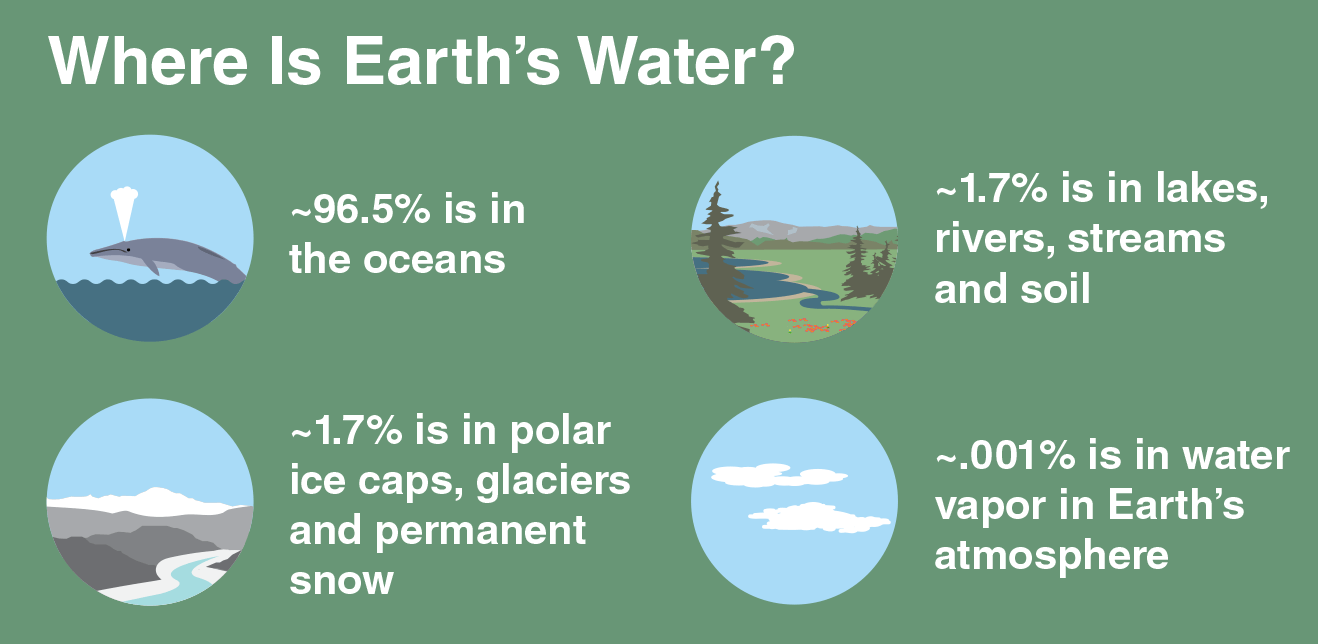
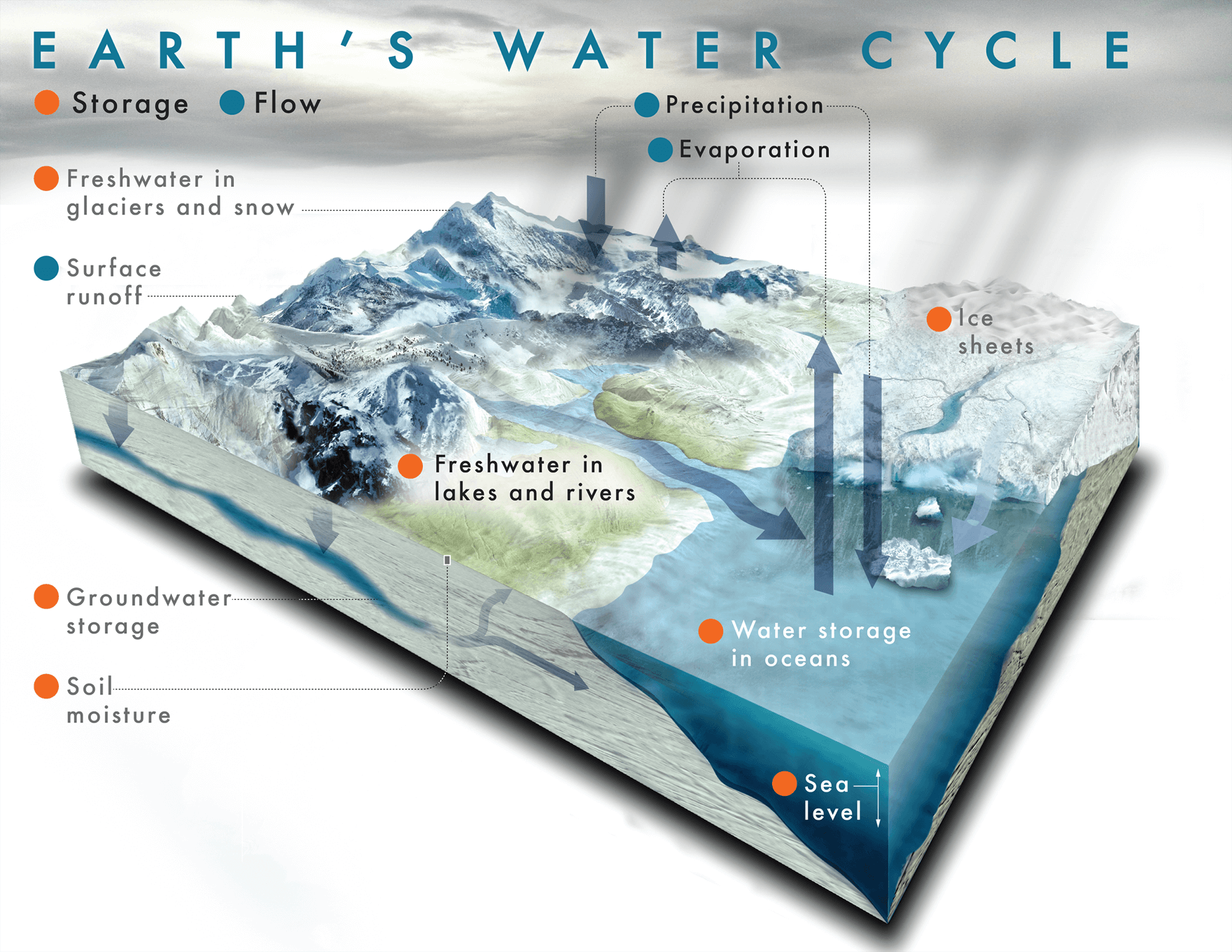
Aim: To learn practical ways of recycling so that we can make our world a better place.
How can we prevent climate change by recycling these products?
Plastics: It prevents climate change by not using coal to burn and release Co2 (Carbon Dioxide).
Cycling or walking: This can prevent climate change by not using vehicles, such as cars. Cars releases smoke which is carbon dioxide. By cycling or walking it is much safer for the environment than cars.
Paper: If we recycle paper it can still be used which means we don't have to cut trees down more ofter since we can use recycled paper than new ones.
Steel: This can also prevent climate change by not using coal to burn and release Co2.
What is Zero Waste? One of the quickest and cheapest ways a community can immediately reduce climate change impact.
What can we do on the planet?

Plastics: It prevents climate change by not using coal to burn and release Co2 (Carbon Dioxide).
Cycling or walking: This can prevent climate change by not using vehicles, such as cars. Cars releases smoke which is carbon dioxide. By cycling or walking it is much safer for the environment than cars.
Paper: If we recycle paper it can still be used which means we don't have to cut trees down more ofter since we can use recycled paper than new ones.
Steel: This can also prevent climate change by not using coal to burn and release Co2.
Video questions:
What is Zero Waste? One of the quickest and cheapest ways a community can immediately reduce climate change impact.
What can we do on the planet?
- Reduce
- Reuse
- Redesign
- Repair
What do we need to recycle? We need to recycle cans, bottles, paper, newspaper, cardboard, and electronics. We can also kind of recycle food scraps for composting. Share stuff.
What does recycling do? It reduces pollution, it prevents global warming and habitat destruction.
How much of our rubbish is food scraps? The percentage of food scraps in our rubbish is 42%.
What does soil do to carbon dioxide in the atmosphere? It absorbs carbon emissions by 3x more than trees.
What do we need to do?
- Make P____lant_____s.
- Have Zero _____Waste______
What is a carbon footprint?
How can you make your Carbon Footprint smaller?
ENERGY SAVING TIPS FILM
Name 4 of the tips.
- Walk instead of using cars if the destination is not that far.
- Save electricity.
- Reuse
- Recycle.
My goals to make my carbon footprint smaller:
- Save electricity
- Reuse
- Recycle
AT WHAT RATES DO DIFFERENT ITEMS DECOMPOSE?
MY INVESTIGATION.

Choose 5 items from the list and investigate them.
You need to answer three questions.
Name: Paper
You need to answer three questions.
Name: Paper
- How long do they take to decompose? They take up to 2 - 4 weeks to decompose
- What resource/fossil fuel are they made from? Paper is made from wood which are from trees.
- How is this resource recycled? Paper is taken to a recycling plant where they can be recycled. The paper is washed with soapy water to remove the ink, staplers, and glue.
- How does this object contribute to climate change? Decomposition paper releases a gas called "methane", which is 84x heat-trapping than carbon dioxide.
Name: Milk Carton
- How long do they take to decompose? They take up to 5 years to decompose.
- What resource/fossil fuel are they made from? They are made from paperboard coated with waterproof plastic.
- How is this resource recycled? They are separated from other types of paper and sent out to paper mills, which turns them into new products.
- How does this object contribute to climate change? They don't contribute to climate change. But the dairy cows and their manure produce gas emissions, which contribute to climate change.
Name: Plastic Bags
- How long do they take to decompose? They take up 10 - 20 years to decompose.
- What resource/fossil fuel are they made from? They are made from crude oil.
- How is this resource recycled? They can be melted down and used to create new batches of plastic bags.
- How does this object contribute to climate change? The bigger the plastic the more gas it gives off.
Name: Glass Bottles
- How long do they take to decompose? They can probably decompose at 500 years or almost never.
- What resource/fossil fuel are they made from? Glass is from a natural resource, which is silica and limestones.
- How is this resource recycled? Glass is sorted by colour and washed to remove any impurities. The glass will be then crushed and melted, and then be molded into new products.
- How does this object contribute to climate change? While recycling glass and get emitted during the production of glass. The materials can contribute to acidification.
Name: Styrofoam
- How long do they take to decompose? They can not decompose.
- What resource/fossil fuel are they made from? Polystyrene is a type of plastic from non-renewable fossil fuels.
- How is this resource recycled? The styrofoam will be shredded into a conveyor belt into a machine.
- How does this object contribute to climate change? They don't contribute to climate change but they do release toxic chemicals into food.




/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/63008350/082_Neuymayer_Channel_icefront.0.jpg)